Summary
In the present day, speed and accuracy are two key drivers for all businesses looking to adopt a data-driven strategy to succeed. To this end, real-time data allows organizations to respond to events when they occur. It facilitates better decision-making, competitive advantages, and greater customer satisfaction. This blog explores real-time data, how it works, and how your business can utilize it to succeed.
Introduction
Data is generated at unmatched levels, from e-commerce platform activities and social interactions to IoT sensors and business processes. However, the real value of this data is not in its volume but in how quickly it can be processed and acted upon to help businesses revolutionize their processes.
This is where real-time data comes into picture. Unlike conventional batch processing, where data is analyzed hours or even days after gathering, real-time data is gathered, processed, and delivered immediately. This helps businesses from different industries make faster decisions, improve customer interaction, detect fraud, and perform predictive maintenance.
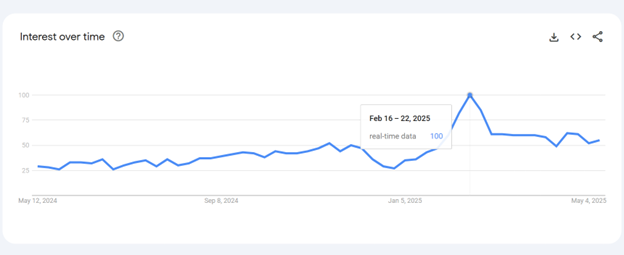
As per the Google Trends report, in February 2025, the worldwide interest over time value of real-time data was 100.
In this blog, we will learn about real-time data, its implementation process, and challenges.
What is Real-Time Data?
Real-time data is information gathered, processed, and presented virtually in real time. This data type enables organizations to react when any event occurs, whether monitoring stock levels, finding security bugs, or tracking transactions.
In contrast to batch data processing, where data gathered is processed subsequently, real-time systems continuously consume and process data with little or no delay. This is beneficial for businesses or applications where timing is everything. One of the best examples of it is ride-sharing services such as Uber. Uber uses real-time data to connect riders with drivers. It also gives details like estimated ETAs and prices based on demand.
Real-Time Data Architecture
A real-time data system requires robust architecture that enables easy data processing for any business with minimal latency. For every real-time data system, some components may vary as per business type and scale. The standard real-time data architecture is as follows –

Real-Time Data Sources
The real-time data sources include the following systems to generate data continuously:
- App Activity: Application activities like user interactions and session logs.
- Server Logs: Server logs include system metrics and errors.
- IoT/Sensors: Sensors of IoT devices data sources include temperature, motion, and machinery data.
- Online Advertising: Online advertisements include real-time data sources like clicks and impressions.
- Clickstream: Clickstreams include user behavior on websites.
These data sources are captured using the CDC streaming tool or other real-time data collection tools, such as Google Cloud Pub/Sub, Apache Kafka, and Amazon Kinesis.
Stream Processing Layer
Once the raw data is ingested from the data sources, it is routed into the stream processing engine, which will help data engineers to execute real-time workflows. In this layer, data-in-motion is filtered and transformed. Here, the data is processed using stream processing tools such as:
- Apache Flink
- Apache Storm
- Apache Spark Streaming
Data Queries and Storage Layer
After processing, data either goes into the query stage or is stored for real-time auditing, analytics, or model training.
- Real-Time Query with KSQL: Here, we have taken an example of KSQL (Kafka SQL). Data engineering companies can use similar SQL engines. At this stage, there might be a case where users can run continuous queries on live data streams. For this, a real-time data approach enables real-time dashboards, alerts, and decision-making systems.
- Relational Data Store for Later Use: Simultaneously, it might happen that the processed data can be written to cloud-based data warehouses like Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, or Snowflake. This will enable data engineers to retain business historical records, combine streaming data, and use enriched datasets to train & refine machine learning models.
Support & Visualization Layer
The last layer is for support and visualization. In this layer, the processed data is made available in real time for dashboards, systems, or users.
- Real-Time Applications
- BI & Analytics Tools
- Machine Learning & AutoML
After understanding the real-time data architecture, let us clearly understand how data is collected.
How is Real-Time Data Collected?
Real-time data collection is about the very first stage of the architecture pipeline. This means that data is collected when it is generated. The process of collecting data is essential as the precision of data gathering has a direct connection with its performance. Therefore, rather than storing data, data engineers prefer to ingest business data into stream processing tools instantly.
There are three types of sources to gather data: user-generated events, sensor data, and enterprise systems or datasets.
For minimal latency and reliability during spikes in data volume of any business, the data collection pipeline also includes the following:
- Decouple consumers or producers through messaging queues or pub/sub systems.
- Schema registries to make sure data structure consistency between two events.
- Batching using lightweight agents.
Types of Real-Time Data
Real-time data can differ significantly in source, use, and form. We have understood real-time data along with its architecture and collection approach. Now, let us know the categories of real-time data that assist organizations in creating improved architectures.
Time-Series Data
Time series data is recorded at intervals and used to monitor business trends over time. It is used extensively in financial analysis, monitoring systems, and IoT. Some examples of time series data are CPU or network usage metrics, Stock market prices, and Patient vitals from health monitors.
Event Data
This type of data is derived from isolated events. For instance, users click on a link or make motion-detected movements. Event data includes metadata as context, timestamps, and IDs. The best example of event data is user login attempts.
Log and Stream Data
Infrastructures, servers, or applications produce this type of data. Understanding user behavior, system performance, and errors is beneficial. Some real-world examples of log and stream data are API call logs, server health metrics, and application error logs.
Geospatial Data
The gathered data is gathered from GPS-enabled devices. This can include movement, coordinates, and location changes in real-time. It is useful for businesses working with transport, logistics, and field services like the construction and manufacturing industries. Examples of geospatial data are delivery route optimization, location-based marketing, and more.
Benefits of Real-Time Data
Here are some of the major benefits of acquiring real-time data.
Better Security & Risk Management
Real-time data enables early detection of threats that can eventually help minimize fraud, regulatory offenses, and cybersecurity threats. For instance, data engineers working for fintech companies and banks block real-time suspicious transactions through analytics.
Quick Data-Driven Decisions
Real-time data enables data engineering companies to make timely and informed decisions. This can help their clients detect delays and work on them before they affect the business. For instance, the data engineering team can guide construction companies to redirect logistics in real time when a delay is detected.
Operational Efficiency
With real-time information, monitoring any system or process can be carried out, which can help avoid downtime and increase productivity.
Improved Customer Experience
Businesses prefer to give personalization to the end-users to boost satisfaction and conversions. For this, real-time data helps understand user behavior and inform recommendations dynamically. The best example of this is online video streaming applications.
Competitive Advantage
Another advantage of leveraging real-time data is having the ability to respond customer activities and market changes faster than anyone else with the help of strategic differentiator.
Use Cases Across Industries
Real-time data has become a priceless resource for several industries due to its capacity to have tailored applications for the optimization of user experiences, operations, and outcomes.
- Finance: Banks and fintech organizations leverage real-time transaction data to provide personalized financial products, reduce fraud, and manage risk.
- Healthcare: Real-time data enables healthcare firms to track devices and wearables in clinics where doctors can view patient vitals and other data in real-time.
- Retail and E-commerce: Retailers and e-commerce organizations have the ability to track customer behavior and shopping patterns.
- Manufacturing: Smart manufacturing is built on real-time data because it needs live information about manufacturing equipment and processes in order to reduce downtime and optimize production lines.
- Transportation and Logistics: Real-time geospatial data supports businesses in the management of delivery, route optimization, and managing vehicle conditions.
Technologies Enabling Real-Time Data
The real-time data ecosystem is supported by some modern technologies like:
- Stream Processing Tools: Apache Storm, Apache Spark Streaming, and Apache Flink.
- Ingestion Platforms: Amazon Kinesis, Apache Kafka, and Google Cloud Pub/Sub.
- Visualization Tools: Granafa, Power BI, and Tableau.
- AI & ML Platforms: Google AutoML and Amazon SageMaker.
How to Implement Real-Time Data in Your Business
Incorporating real-time data into your business takes both business alignment and technical infrastructure. Here is how you can implement real-time data.
- Establish Use Cases: Find out where real-time data can bring the most value and start with customer-facing operations, mission-critical monitoring, and risk-sensitive processes.
- Establish the Proper Data Infrastructure: As per the scale of your business, choose the suitable ingestion, streaming, and processing tools. Prioritize the use of cloud-based platforms to have a scalable business process.
- Data Governance and Quality: Make sure that all the schema registries and data contracts are in accordance with data governance and quality. Implement policies for real-time privacy, compliance, and auditability.
- Start with Small and Scale Up Gradually: When implementing real-time data, start with small projects. Later, deploy the same approach across departments. This can help businesses focus on high-impact wins first to create momentum and justify investment.
- Integration with BI and Decision-making Systems: To have maximum responsiveness, make sure your dashboards, automation systems, and application alerts are integrated with the stream of real-time data.
Challenges in Implementing Real-Time Data
With advantages, real-time data implementation also comes with some challenges. And they are –
- Integration with Legacy Systems
- Infrastructure Complexity
- Latency Sensitivity
- Data Consistency and Accuracy
- High Costs
Conclusion
As seen in this blog, real-time data is the base for quick decision-making, tailored customer experience, and business brilliance. Manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and logistics are sectors where real-time data is being taken up to be competitive. By successfully putting into place a roadmap for real-time, the challenges inherent in it are overcome. Reach out to the Aezion data engineering team to ride the waves of a real-time data analysis method.
FAQs
How is real-time data different from batch data?
Real-time data is processed in real time as it’s generated, while batch data is collected and processed in batches.
What is an example of real-time data?
The best example of real-time data is following a delivery on a logistics app. The app updates the package’s location as GPS data shifts.
Which technologies are used to process real-time data?
Apache Kafka, Flink, Spark Streaming, Amazon Kinesis, and Google Cloud Dataflow are key technologies used to process real-time data.
Why is real-time data important for businesses?
Real-time data allows businesses to react in real time. It also provides faster, data-driven decision-making, detecting fraud, improving customer experience, and operational excellence.
Is real-time data more costly to deploy?
Yes, it usually is more expensive in terms of infrastructure, but once installed, it pays back the cost for high-value applications.




